×
×
If 3-way air valves seem confusing, you’ll find that they are in fact very simple once you know how they work. These are the valves used to regulate airflow in a pneumatic system. They have three ports, allowing the air to flow in various orientations depending on how the valve is positioned.
An air powered 3-way valve operates by applying pneumatic pressure to guide the path of the air. When blowing air into the valve, it causes a mechanism inside the valve to shift around, controlling where the forced air exits out of the valve. You can turn the valve to direct the air where you want it to go, so you can control the motion of the pneumatic cylinders or other pneumatic devices in your system.
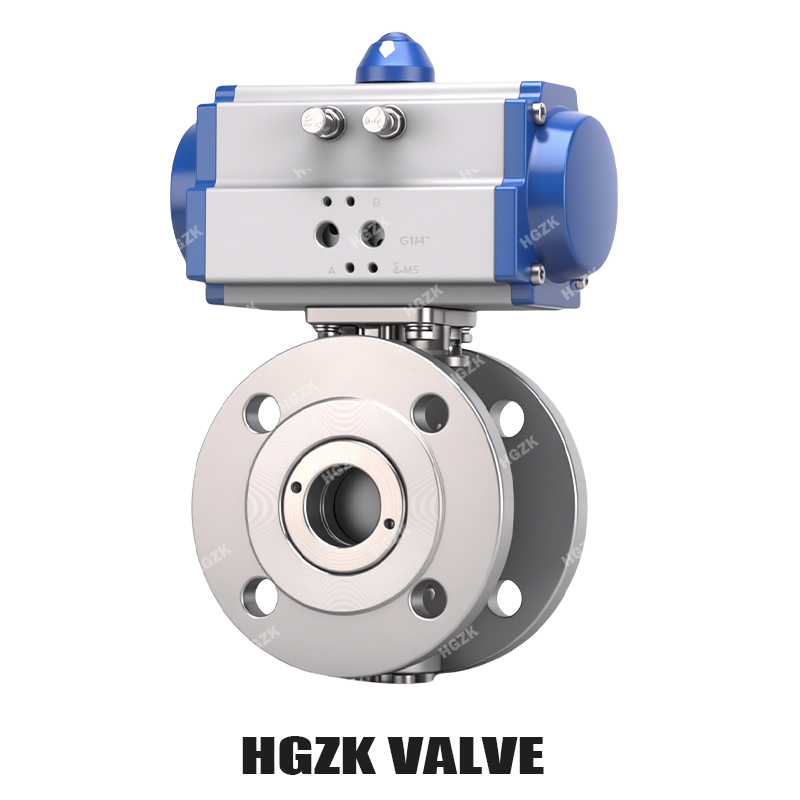

There are a number of advantages to using air operated 3-way valves in your pneumatic system. They are easy to use and maintain One of the main advantages of these materials is that they are straight forward and reliable. They also permit rapid and accurate adjustment of air flow, when such an ability is important for an application. What’s more, they are the most economical compared with other types of valves, which is beneficial for users.
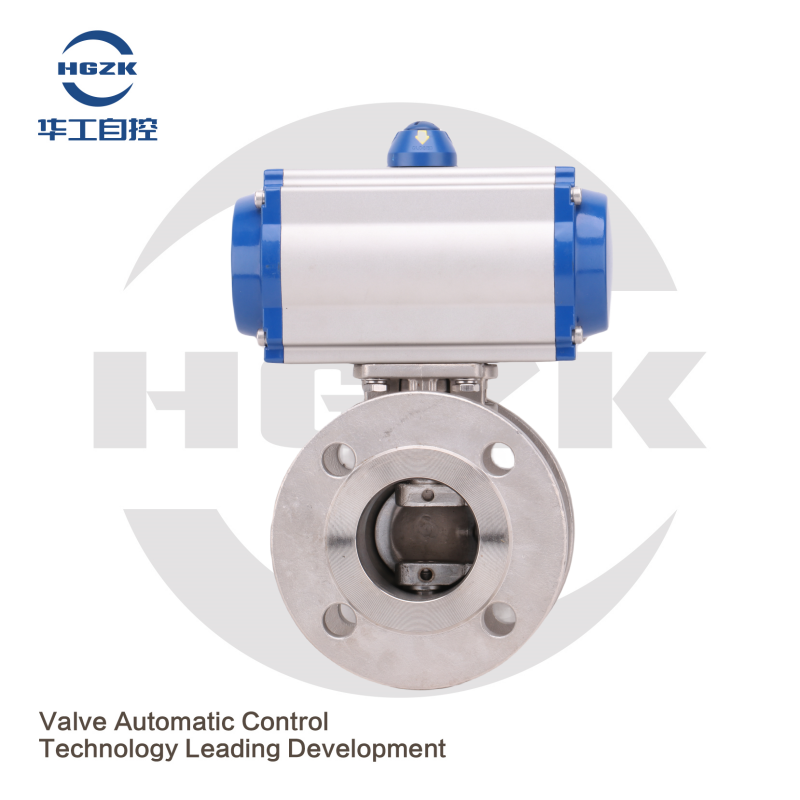

The applications for a 3 way air operated valve are endless. One example is in industrial production where they are employed to actuate, or move, pneumatic cylinders on manufacturing lines. They are used in the automotive, food, and pharmaceutical industries. In the automotive field, for instance, they can be employed to control air flow in various portions of an automobile pneumatic system.
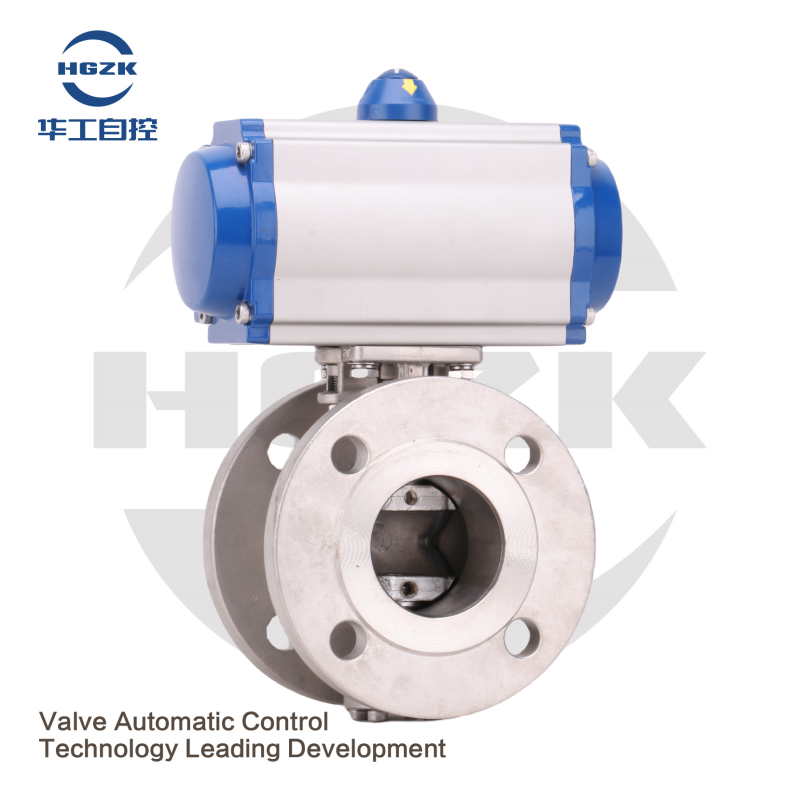

Troubleshooting Your Air-Operated 3-Way Valve If you are experiencing issues with an air-operated 3-way valve, there are a few things you can check to try to diagnose the problem. First, check to see that the valve has an abundant supply of compressed air. The valve will fail to operate if the air pressure is not sufficient. You will also need to look for any leaks in the system that could be causing the valve to malfunction. Lastly, ensure that the valve is adequately lubed, failure to do so can lead to the movement inside the valve to seize solid.
Guidance Support. team of experts committed offering guidance support. Should need assistance selecting right product technical air operated 3 way valve problem-solving, we're ready to assist you in every step. Quick Response ResolutionWe provide prompt and effective support when problems arise. This includes prompt responses to inquiries and concerns from customers about product specifications and technical support.
committed offering users' system-matching selection and configuration solutions that maximize the benefits of technology by using modern technology as a guide. From the initial design phase packaging products processed and customized to meet the requirements customers. We also provide scientific management service that is one-stop and allows us to consistently release high-quality products.We provide wide range materials and actuators. These valves in a air operated 3 way valve of materials including PVDF, PP, PVC, stainless steel, cast iron and cast steel, as well as brass. The valves are operated with hand, pneumatic, electrical, or hydraulic actuators.
Professional Manufacturer. are a specialist in AUTO Control Valves we utilize knowledge, experience and latest technologies offer top-quality products at low prices. Variety of Products. provide a broad range of actuators and valves designed meet demands various industries applications and meeting various requirements of our clients. Customized Solutions. With our strong capabilities for customization, we offer a variety solutions, OEM/ODM options satisfy your unique branding and engineering requirements and ensure air operated 3 way valve integration into your pipelines. Technical Support. Our team of experts has vast technical know-how and provides professional assistance and support in order to ensure our customers know how to utilize our products correctly.
Welcome HGZK VALVE, a leading innovator in Fluid Control solutions. specialize designing manufacturing, manufacturing, and selling the full range of valve products, such as pneumatic and electric valves actuators. supply products worldwide to meet the air operated 3 way valve of diverse industries. products designed using the latest CAD 3D design system, which not only has a gorgeous appearance but also offers dependable quality. A large number of precision CNC machining centers are used in machines to ensure the accuracy of the components and form a large-scale production capacity. The machines are used in a variety of regulating valves, ball valves, butterfly valves gate valves, slurry valves, globe valves, plug valves and many other valves.